All Image courtesy of Service Objects – ZIP Code

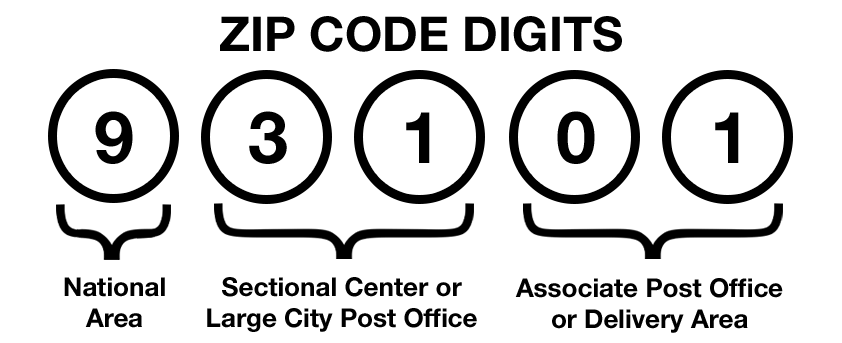
Not So Random: While they may seem arbitrary, each digit in a ZIP code holds meaning! The first digit broadly categorizes a geographic region (e.g., 0 for the Northeast, 9 for the West). The next two digits narrow it down to a specific area, and the final two pinpoint a local post office or delivery route.
Beyond Mail Delivery: ZIP codes are more than just for sending letters! They play a crucial role in emergency services, tax forms, online shopping, and even marketing campaigns. Knowing your ZIP code ensures you get the right services and targeted information.
The Shortest and the Longest: Not all ZIP codes are created equal! The shortest ZIP code belongs to the Internal Revenue Service in Holtsville, NY (00501). The longest, meanwhile, goes to Ketchikan, Alaska (99950) – perhaps an extra digit is needed for all that beautiful wilderness!
Presidential Perks: Talk about exclusive ZIP codes! The White House has its own unique code (20500), with additional codes for specific areas within the complex, like the Greetings Office. Even Smokey Bear, the U.S. Forest Service mascot, has his own special ZIP code (20252).
A Code for Everything (Almost): While most people have a ZIP code for their residence, there are unique codes for specific situations. For instance, P.O. Boxes have their own ZIP codes, and military bases use a special format to ensure efficient mail delivery to personnel stationed around the world.
The Rise of the ZIP+4: In 1991, ZIP codes got an upgrade with the introduction of ZIP+4 codes. These additional four digits pinpoint specific delivery points, like a particular floor in a large building, further streamlining mail sorting and delivery.
From Two Digits to Five: Believe it or not, ZIP codes weren’t always five digits long! The original system in 1943 used just two digits to designate broad geographic zones. As mail volume grew, the need for a more precise system led to the five-digit format adopted in 1963.
Meet Mr. ZIP: In the 1960s, the USPS launched a memorable campaign to promote the new ZIP code system. Their mascot, Mr. ZIP, a friendly cartoon postman, encouraged people to use ZIP codes and helped educate the public about their importance.
Beyond the US Borders: While ZIP codes are specific to the United States, many other countries have adopted similar postal codes. These codes serve the same purpose of facilitating efficient mail delivery and sorting within their respective national postal systems.
The Future of ZIP Codes: In today’s digital age, the role of traditional mail might be changing, but ZIP codes are likely here to stay. They continue to play a vital role in various aspects of our lives, and with innovations like barcode technology, their efficiency is only going to improve.
The ubiquitous ZIP code, a seemingly simple string of digits, plays a crucial role in our daily lives. But how did this system come to be? Let’s delve into the fascinating history of ZIP codes, exploring their invention and implementation.
The Seeds of Change: A Need for Efficiency
Prior to the 1940s, mail delivery relied on a rudimentary system of zone numbers for large cities. However, a surge in mail volume due to World War II exposed the limitations of this approach. Experienced postal clerks were being deployed, leaving a gap in expertise for efficiently sorting the ever-increasing amount of mail.
The Birth of an Idea: Enter Postal Inspector Robert Moon
In 1944, a visionary postal inspector named Robert Moon stepped onto the scene. Recognizing the need for a more efficient system, Moon proposed a national three-digit code system. Each code would designate a specific geographical area, allowing even less experienced clerks to sort mail with greater speed and accuracy.
The Road to Implementation: Overcoming Resistance
While Moon’s idea held merit, it faced initial resistance from within the postal service. Some viewed it as an unnecessary complication, and others worried about the cost of implementation. However, Moon’s persistence and the urgency of the situation ultimately prevailed.
From Concept to Reality: The Rise of the Five-Digit Code
In 1962, Postmaster General J. Edward Day, recognizing the potential of Moon’s plan, decided to take it a step further. He proposed a five-digit code system, combining Moon’s three-digit zones with existing two-digit local zones. This enhanced system offered even greater precision in mail sorting and delivery.
Winning Over the Public: The Introduction of Mr. ZIP
To ensure the success of the new system, the USPS launched a public education campaign in 1963. Enter Mr. ZIP, a friendly cartoon mail carrier, who became the face of the campaign. Through educational materials and catchy slogans like “Use ZIP Code,” Mr. ZIP encouraged the public to adopt the new system.
Putting it All Together: The Transition and Beyond
The transition to ZIP codes wasn’t instantaneous. Initially, their use was voluntary. However, the benefits of faster and more accurate delivery became evident. By the late 1960s, ZIP codes were widely adopted, revolutionizing mail delivery in the United States.
A Legacy of Efficiency: The Enduring Role of ZIP Codes
Today, ZIP codes are an integral part of our daily lives. They not only facilitate mail delivery, but also play a crucial role in emergency services, tax forms, online shopping, and even marketing campaigns. The innovation of Robert Moon, coupled with the foresight of the postal service, has left a lasting impact on how information and goods reach their destinations.
A Glimpse into the Future: Adapting to Change
While the rise of digital communication has changed how we interact, physical mail remains relevant. ZIP codes, with their potential for integration with barcode technology and other innovations, are likely to continue playing a vital role in ensuring efficient mail delivery even in the digital age.
For home page click here and for pin codes click here
